IOC PostProcessor && Aware
TODO
@Bean && <bean/> 阶段
用户使用注解或XML方式编写注册Bean
Spring通过BeanDefinitionReader将Bean解析成BeanDefinition BeanDefinitionRegistry.registry注入容器?只注入几个Loader?
- AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader
- XmlBeanDefinitionReader
- GroovyBeanDefinitionReader
- @Deprecated PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader
执行位置
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#run(java.lang.Class<?>, java.lang.String…)
->
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#run(java.lang.Class<?>[], java.lang.String[])
->
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#run(java.lang.String…)
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#prepareContext
pringframework.boot.SpringApplication#load
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130/**
* Create a new {@link BeanDefinitionLoader} that will load beans into the specified
* {@link BeanDefinitionRegistry}.
* @param registry the bean definition registry that will contain the loaded beans
* @param sources the bean sources
*/
BeanDefinitionLoader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object... sources) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "Registry must not be null");
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
this.sources = sources;
this.annotatedReader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(registry);
this.xmlReader = (XML_ENABLED ? new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(registry) : null);
this.groovyReader = (isGroovyPresent() ? new GroovyBeanDefinitionReader(registry) : null);
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(registry);
this.scanner.addExcludeFilter(new ClassExcludeFilter(sources));
}
/**
* Factory method used to create the {@link BeanDefinitionLoader}.
* @param registry the bean definition registry
* @param sources the sources to load
* @return the {@link BeanDefinitionLoader} that will be used to load beans
*/
protected BeanDefinitionLoader createBeanDefinitionLoader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object[] sources) {
return new BeanDefinitionLoader(registry, sources);
}
/**
* Load beans into the application context.
* @param context the context to load beans into
* @param sources the sources to load
*/
protected void load(ApplicationContext context, Object[] sources) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loading source " + StringUtils.arrayToCommaDelimitedString(sources));
}
BeanDefinitionLoader loader = createBeanDefinitionLoader(getBeanDefinitionRegistry(context), sources);
if (this.beanNameGenerator != null) {
loader.setBeanNameGenerator(this.beanNameGenerator);
}
if (this.resourceLoader != null) {
loader.setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader);
}
if (this.environment != null) {
loader.setEnvironment(this.environment);
}
loader.load();
}
//loader.load(); for循环进入,只有启动类
private void load(Object source) {
Assert.notNull(source, "Source must not be null");
if (source instanceof Class<?>) {
load((Class<?>) source);
return;
}
if (source instanceof Resource) {
load((Resource) source);
return;
}
if (source instanceof Package) {
load((Package) source);
return;
}
if (source instanceof CharSequence) {
load((CharSequence) source);
return;
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid source type " + source.getClass());
}
//load((Class<?>) source);
private void load(Class<?> source) {
if (isGroovyPresent() && GroovyBeanDefinitionSource.class.isAssignableFrom(source)) {
// Any GroovyLoaders added in beans{} DSL can contribute beans here
GroovyBeanDefinitionSource loader = BeanUtils.instantiateClass(source, GroovyBeanDefinitionSource.class);
((GroovyBeanDefinitionReader) this.groovyReader).beans(loader.getBeans());
}
if (isEligible(source)) {
this.annotatedReader.register(source);
}
}
//load((Resource) source);
private void load(Resource source) {
if (source.getFilename().endsWith(".groovy")) {
if (this.groovyReader == null) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Cannot load Groovy beans without Groovy on classpath");
}
this.groovyReader.loadBeanDefinitions(source);
}
else {
if (this.xmlReader == null) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Cannot load XML bean definitions when XML support is disabled");
}
this.xmlReader.loadBeanDefinitions(source);
}
}
//load((Package) source);
private void load(Package source) {
this.scanner.scan(source.getName());
}
//load((CharSequence) source);
private void load(CharSequence source) {
String resolvedSource = this.scanner.getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(source.toString());
// Attempt as a Class
try {
load(ClassUtils.forName(resolvedSource, null));
return;
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException | ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// swallow exception and continue
}
// Attempt as Resources
if (loadAsResources(resolvedSource)) {
return;
}
// Attempt as package
Package packageResource = findPackage(resolvedSource);
if (packageResource != null) {
load(packageResource);
return;
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid source '" + resolvedSource + "'");
}org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#registerBeanDefinition
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");
Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null");
if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
try {
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);
}
}
BeanDefinition existingDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (existingDefinition != null) {
if (!isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionOverrideException(beanName, beanDefinition, existingDefinition);
}
else if (existingDefinition.getRole() < beanDefinition.getRole()) {
// e.g. was ROLE_APPLICATION, now overriding with ROLE_SUPPORT or ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Overriding user-defined bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a framework-generated bean definition: replacing [" +
existingDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else if (!beanDefinition.equals(existingDefinition)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a different definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with an equivalent definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
else {
if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) {
// Cannot modify startup-time collection elements anymore (for stable iteration)
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
List<String> updatedDefinitions = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames.size() + 1);
updatedDefinitions.addAll(this.beanDefinitionNames);
updatedDefinitions.add(beanName);
this.beanDefinitionNames = updatedDefinitions;
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
}
else {
// Still in startup registration phase
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
}
if (existingDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) {
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
else if (isConfigurationFrozen()) {
clearByTypeCache();
}
}GroovyBeanDefinitionReader, PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader, XmlBeanDefinitionReader会进行调用loadBeanDefinitions,AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader没有实现BeanDefinitionReader接口,因为AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader没有必要解析Spring的Resource类型,只要扫描jar包的class文件就可以
org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader#loadBeanDefinitions(org.springframework.core.io.support.EncodedResource)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38/**
* Load bean definitions from the specified XML file.
* @param encodedResource the resource descriptor for the XML file,
* allowing to specify an encoding to use for parsing the file
* @return the number of bean definitions found
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors
*/
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource);
}
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
try (InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream()) {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
finally {
currentResources.remove(encodedResource);
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
}
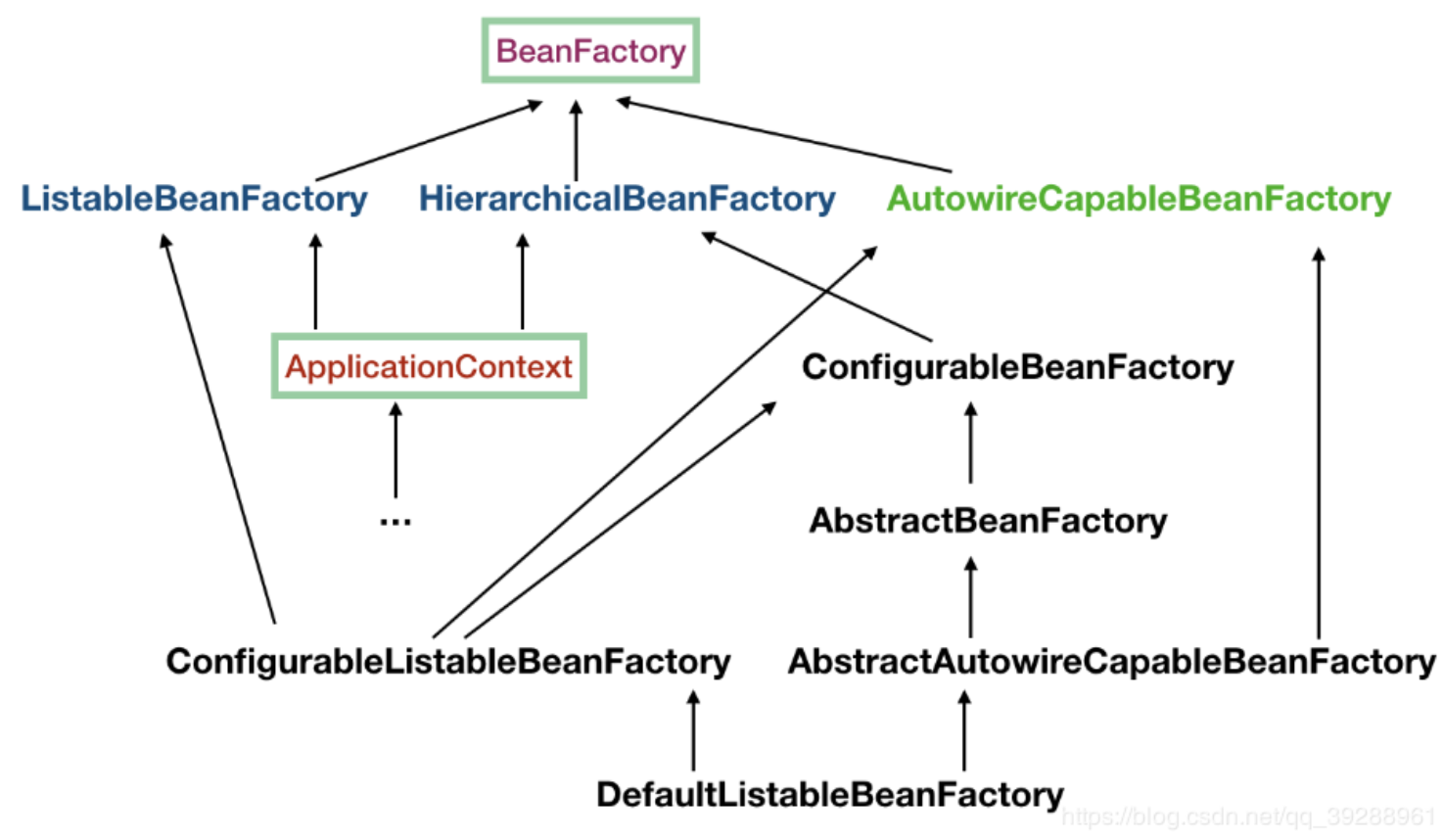
BeanDefinition 阶段
BeanFactory
- 构建Bean工厂
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
- 获取BeanDefinition
- 删除BeanDefinition
- 替换,BeanDefinitionBuilder.build().register.regist() 设置自己的Bean定义/实现类
作为BeanFactoryPostProcessor子类执行优先级更高的原因
都是IOC容器创建调用refresh接口
都调用到invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)方法
从容器中获取到所有的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor组件。
依次触发所有的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry()
再触发postProcessBeanFactory()方法BeanFactoryPostProcessor
因此优先于BeanFactoryPostProcessor
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
reiterate = true;
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
//先触发postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
// Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
//在此触发postProcessBeanFactory
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
再从容器中找到BeanFactoryPostProcessor组件,然后依次触发postProcessorBeanFactory()方法
1 | public interface BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor { |
BeanFactoryPostProcessor
对BeanFactory本身的设置(BeanFactory的后置处理器)
在BeanFactory
标准初始化之后调用。所有的BeanDefinition已保存加载到BeanFactory中,但Bean Instance仍未创建时机:IOC容器创建对象 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)
- org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#refresh
- org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
- org.springframework.context.support.PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, java.util.List<org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor>)
- org.springframework.context.support.PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(java.util.Collection<? extends org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor>, org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory)
- org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor#postProcessBeanFactory
如何找到所有的BeanFactoryPostProcessor并执行他们的方法
- 直接在BeanFactory容器中找到所有类型是BeanFactoryPostProcessor的组件,并执行它们的方法
- 在
初始化创建其他組件前面执行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
* 标准初始化之后调用
* Modify the application context's internal bean factory after its standard initialization.
* 所有的BeanDefinition已保存加载到BeanFactory中,但Bean Instance仍未创建
* All bean definitions will have been loaded, but no beans will have been instantiated yet.
* 允许覆盖或添加属性,甚至是eager-initializing beans
* This allows for overriding or adding properties even to eager-initializing beans.
* @param beanFactory the bean factory used by the application context
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
}
MessageSource
- 执行位置
- org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#refresh
- org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#initMessageSource
ApplicationEventMulticaster
- 事件多播器
- 执行位置
- org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#refresh
- org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#initApplicationEventMulticaster
ApplicationListener
- 监听容器中发布的事件,完成事件驱动模型的开发
- 监听ApplicationEvent及其下面的子事件
- 原理:ContextRefreshedEvent事件
- 容器创建对象 AbstractApplicationContext #refresh()
- 容器刷新完成 AbstractApplicationContext #finishRefresh()
- AbstractApplicationContext #publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this))
- 获取 EventMulticaster : getApplicationEventMulticaster()
- multicaster派发事件
- 获取所有的ApplicationListener 根据是否含有Executor判断同步/异步 进行for循环派发
- 执行位置
- org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#refresh
- org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#finishRefresh
- org.springframework.context.LifecycleProcessor#onRefresh
- org.springframework.context.support.DefaultLifecycleProcessor#startBeans
- org.springframework.context.support.DefaultLifecycleProcessor.LifecycleGroup#start
- org.springframework.context.support.DefaultLifecycleProcessor#doStart
- org.springframework.context.Lifecycle#start
- org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#publishEvent(org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent)
- org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster#multicastEvent(org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent, org.springframework.core.ResolvableType)
- org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster#invokeListener
- org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster#doInvokeListener
- org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener#onApplicationEvent
1 |
|
Instantation
Populate && Initialization
Aware
InvokeAware调用部分
- BeanNameAware
- BeanClassLoaderAware
- BeanFactoryAware
IOC完整生命周期
BeanNameAware
BeanClassLoaderAware
BeanFactoryAware
EnvironmentAware
EmbeddedValueResolverAware
ResourceLoaderAware
ApplicationEventPublisherAware
MessageSourceAware
ApplicationContextAware
ApplicationStartupAware
ServletContextAware
LoadTimeWeaverAware
ImportAware
BeanPostProcessor
Bean后置处理器,Bean对象创建初始化
前后进行拦截工作的解析自定义注解
Spring对BeanPostProcessor使用
- Bean赋值
- 注入其他组件
- @Autowired
- 生命周期注解功能
- @Async
- …
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14public interface BeanPostProcessor {
//在初始化之前工作
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
//在初始化之后工作
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
}
Populate-Aware-PostProcessor调用步骤
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#refresh
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#finishBeanFactoryInitialization
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory#getBean(java.lang.String)
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory#doGetBean
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry#getSingleton(java.lang.String, org.springframework.beans.factory.ObjectFactory<?>)
—>
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean(java.lang.String, org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition, java.lang.Object[])
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean
1
2
3
4
5
6try {
//填充属性 autowireByName autowireByType
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
//初始化Bean
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#initializeBean(java.lang.String, java.lang.Object, org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
//调用BeanNameAware、BeanClassLoaderAware、BeanFactoryAware
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//初始化前
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
//InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//初始化后
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
Created
Destroy
ApplicationContext
其他 Bean 和进行其他的的上下文初始化
实例化剩余的 Bean 单例
ApplicationContextAware
- 存储全局ApplicationContext